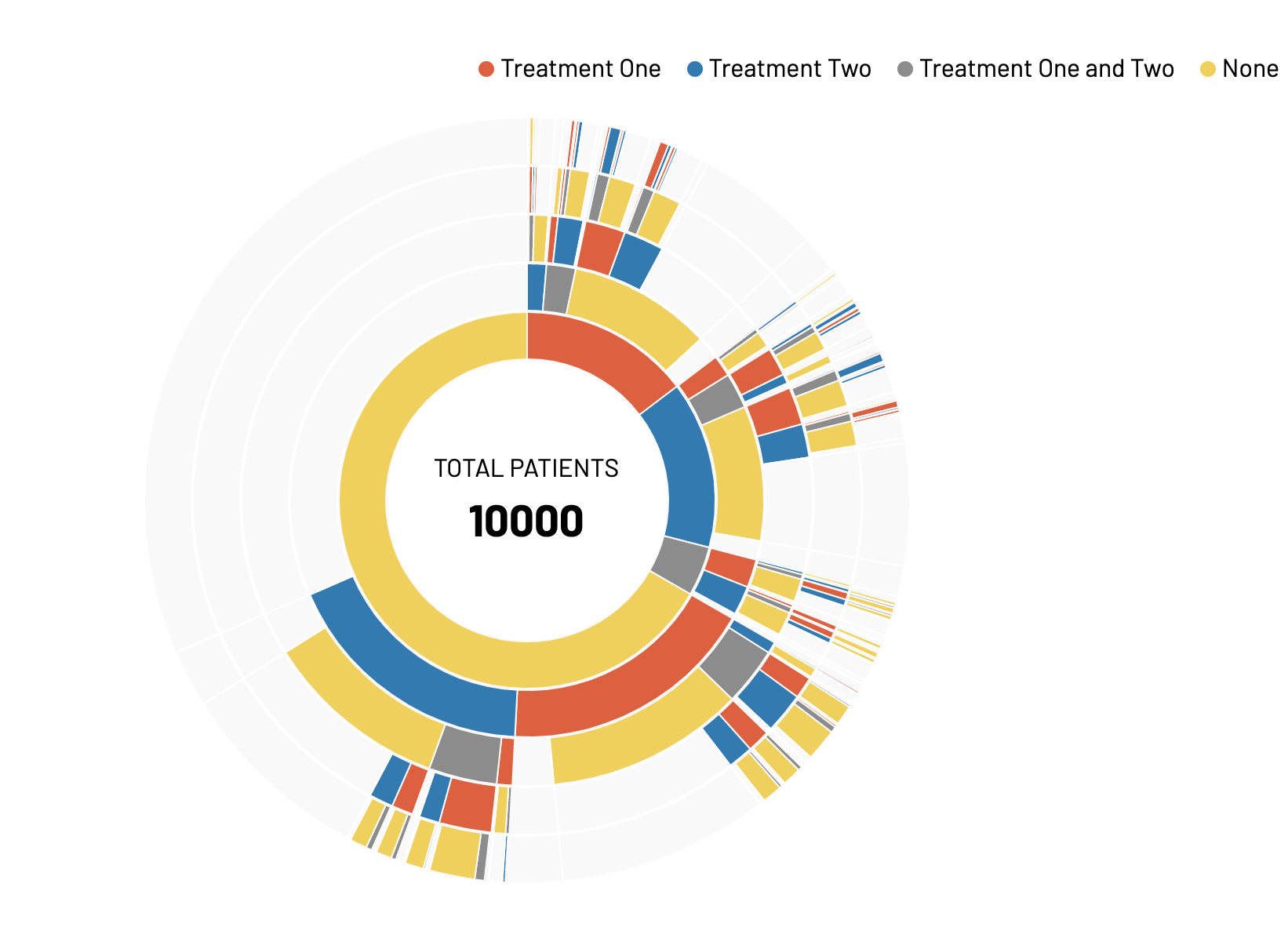
Overview
Sunbursts are similar to Sankeys in that they visualize patterns, but differ in how the patterns are calculated. In Sankeys, states are calculated at cross-sectional points in time and presented as flows through time. In sunbursts, order, irrelevant to time, is considered in calculation of the pattern. For example, a patient who is on Treatment A for one year then Treatment B for one day would have the exact same pattern as someone who is on Treatment A for one day, then transitions to Treatment B for one year (A -> B).
Basic Sunburst
First, the id level data are created used
sunburst_id_data. This is to help facilitate running on
partitions on the id-level first, before the summarizing step in
sunburst_maker. sunburst_id_data requires a
cohort, an ansible style data.frame, and which “states” are
wanted. It returns a list of the resulting data.frame and the states, so
it can directly be fed into sunburst_maker.
events <- nsSank::convert_tagged_cdf(cdf)
data <- nsSank::ansible(events)
data
#> # A tibble: 57,999 × 4
#> patient_id start end state
#> <int> <date> <date> <list>
#> 1 1 2010-01-01 2010-01-09 <chr [1]>
#> 2 1 2010-01-10 2010-02-09 <chr [2]>
#> 3 1 2010-02-10 2010-02-15 <chr [1]>
#> 4 1 2010-02-16 2010-03-15 <chr [2]>
#> 5 1 2010-03-16 2010-03-18 <chr [3]>
#> 6 1 2010-03-19 2010-03-27 <chr [2]>
#> 7 1 2010-03-28 2010-04-27 <chr [3]>
#> 8 1 2010-04-28 2010-05-04 <chr [2]>
#> 9 1 2010-05-05 2010-06-14 <chr [1]>
#> 10 1 2010-07-17 2010-09-28 <chr [1]>
#> # … with 57,989 more rows
sdata <- nsSank::sunburst_id_data(cohort, data, states = c("a", "b"))
#sdata$id_data
sunburst_list <- nsSank::sunburst_maker(cohort, sdata, max_levels = 5)
nswidgets::create_sunburst(sunburst_list$data, sunburst_list$types)